Cannabinoids Explained
A glimpse into the world of Cannabinoids
Terpenes
Inside of our bodies’ central and peripheral nervous systems, exist a network of cell receptors known as the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Special molecules made by our bodies, called endocan nabinoids, fit like a key into these receptors, activating many different cellular functions that may be crucial to a well-balanced system. Amazingly, Cannabis plants produce phytocannabinoids that after being heated and ingested, or inhaled, bind to those same cell receptors in our bodies. At which point phytocannabinoids produce medical effects.
THCA, like natural acid forms of other cannabinoids, has limited effects until decarboxylated into its neutral form. But unlike all other known cannabinoids, only THC is psychoactive (it gets you ‘high’). Because THC is the only known strongly psychoactive cannabinoid, other cannabinoids may be utilized if psychoactivity is contraindicated.
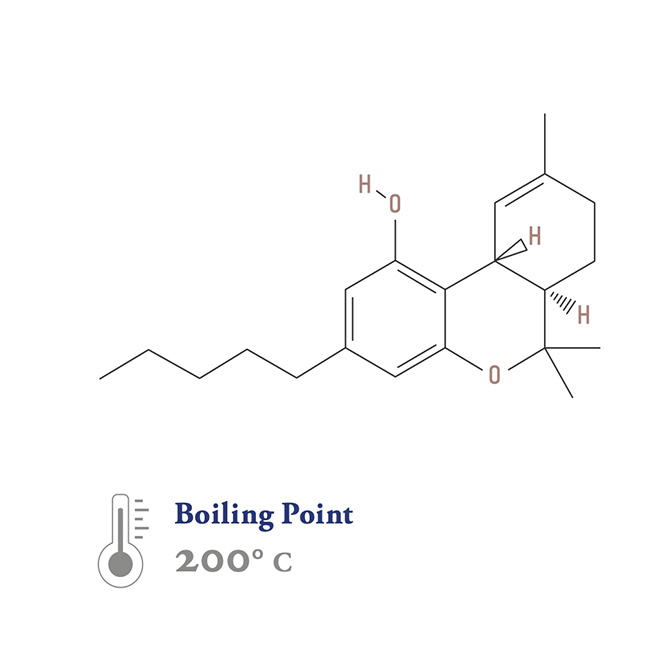
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
tet·ra·hy·dro·ca∙nab∙i∙nol
THC, among its other purported benefits, encourages appetite, may be anti-inflammatory, affect tumor growth, offer insomnia relief, and may be anti- spasmodic. THC is the most abundant secondary metabolite found in drug biotype Cannabis, comprising as much as 30% of the dry weight of unpollinated (sensimilla) flowers. Most ‘high THC’ strains, when grown and harvested optimally, produce about 15% THCA and THC* by dry weight, although this can vary widely. The technical name for THC is Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, or delta-9 THC.
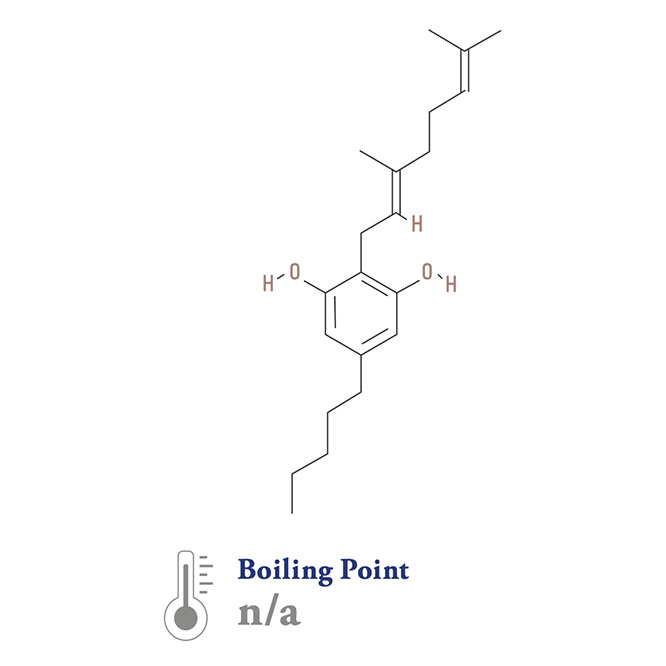
Cannabidiol (CBD)
ca∙nab∙i∙di·ol
Cannabidiol is the second most abundant cannabinoid found in Cannabis. It became well known after it gained attention from the scientific community as an effective treatment for seizure disorders, including those associated with multiple sclerosis and epilepsy. Further study has shown that, in some cases, CBD may be as effective as THC in the management of pain. CBD may lower blood sugar, and has shown promise in the treatment of diabetes. It can promote feelings of calm, may be useful in the treatment of stress disorders, and sleep loss. And it may offer powerful anti-inflammatory properties, particularly effective in the relief of joint pain, or as a treatment for autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. CBD may offer anti-psychotic properties. Additionally, it modulates the effects of THC, often improving the medical efficacy of THC while reducing its psychoactivity.
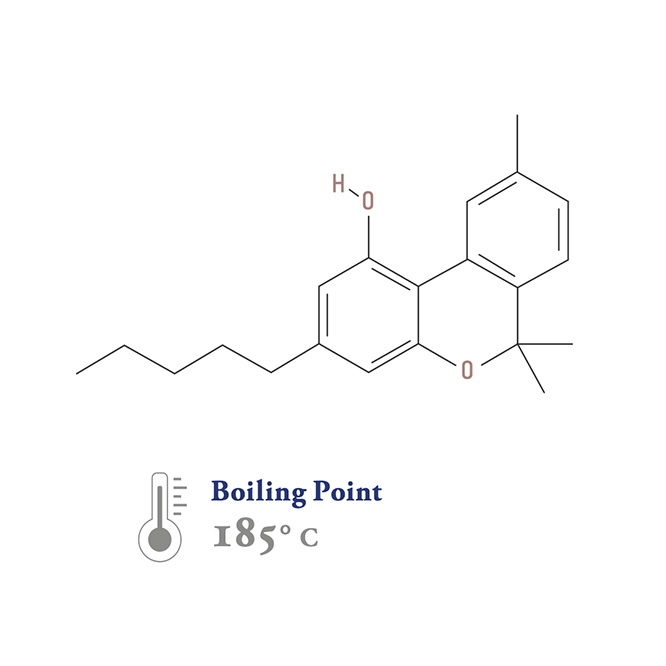
Cannabinol (CBN)
ca∙nab∙i∙nol
Most cannabinol is created when THC is degraded by oxidation (old, poorly stored) or heat (over decarboxylated). CBN is known to be more sedative and narcotic than other cannabinoids, and may be mildly-psychoactive. CBN may be useful to treat insomnia, and act as an anti-convulsant.
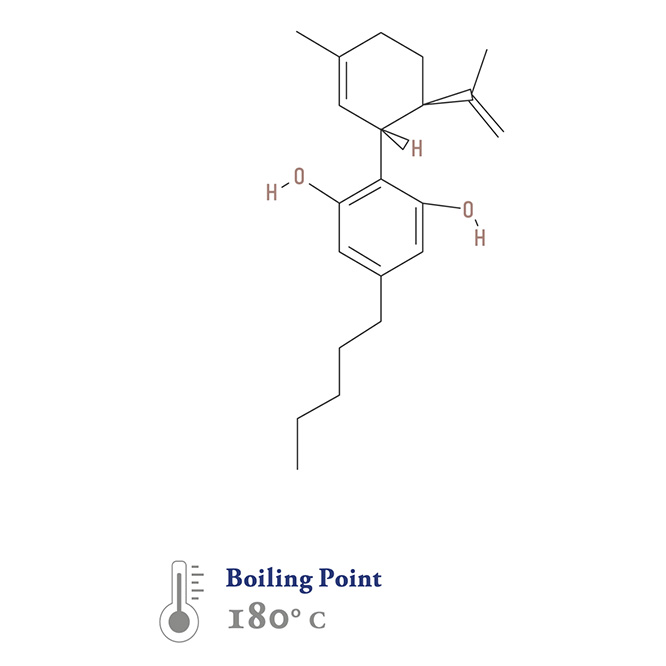
Cannabigerol (CBG)
ca∙nab∙i∙ger·ol
CBG may offer unique neuro-regenerative medicinal effects. It may stimulate bone growth, offer anti-bacterial and anti-tumor properties, and insomnia relief. CBGA is the precursor to all other cannabinoids, like THCA, CBDA, and CBCA, so CBGA is often found in low concentrations.
Cannabichromic Acid (CBC)
ca∙nab∙i∙ger·ol
CBC may be more effective than CBD in treating anxiety and stress. It also shows promise in treating inflammation, offering pain relief, anti-viral, and anti-tumor properties. CBC has been found to stimulate the growth of bone tissue.
ORDER NOW
